Table of Contents
2.A.5.b - Construction and Demolition
Short description
| Category Code | Method | AD | EF | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.A.5.b | T1 | NS | CS | ||||||||||||
| NOx | NMVOC | SO2 | NH3 | PM2.5 | PM10 | TSP | BC | CO | Pb | Cd | Hg | Diox | PAH | HCB | |
| Key Category: | - | - | - | - | -/- | L/T | L/- | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
For particulate emissions, Construction is the second main emissions source in the Mineral industries.
Methodology
Since the last update of the UNECE Guidebook we use the Tier 1 method to estimate the national emissions of particulate matters. The approach for uncontrolled fugitive emissions for this source category was adapted for national circumstances within a research Project (Umweltbundesamt, 2016) 1), partly considered exiting control techniques. As a result, the information of the statistics is combined with modified default emission factors for TSP and PM.
Activity data
Activity data are determined taking into account figures for various construction activities. Data is based on production statistics (national statistics). According to the method used, figures of area of land affected by construction activities per building were concluded from statistical data and multiplied with emission factors, as explained below. The common uncertainty of 3% for national statistics could be increased as a result of this calculation, but the effect is not estimated at the moment.
Emission factors
The emission factors used are results of Adaptation of UNECE-Defaults (EEA, 2016) 2), see chapter NFR 2.A.5.b for different kind of buildings.
Table 1: Overview of apllied emission factors
| Kind of building | Pollutant | EF value | Unit | EF trend | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| single and two family houses | TSP | 0.0638 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| single and two family houses | PM₁₀ | 0.0191 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| single and two family houses | PM₂.₅ | 0.0019 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| apartment buildings | TSP | 0.329 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| apartment buildings | PM₁₀ | 0.099 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| apartment buildings | PM₂.₅ | 0.0099 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| non-residential | TSP | 0.631 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| non-residential | PM₁₀ | 0.189 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| non-residential | PM₂.₅ | 0.0189 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| roads | TSP | 1,674 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| roads | PM₁₀ | 502 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
| roads | PM₂.₅ | 50.2 | kg/m²*y | constant | ||||||
Several further assumptions were necessary to use the formula of the Guidebook:
| EM = EF*B*f*m |
The EF is adapted with Moisture Level Correction factor and Silt Content Correction factor in all cases, both 0.20 and 2.22. The assumption about the duration of the construction activity uses the Default values (EEA, 2016)3):
| Type of building | Estimated duration (year) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction of houses (single and two family) | 0.5 (6 months) | ||
| Construction of apartments (all types) | 0.75 (9 months) | ||
| Non-residential construction | 0.83 (10 months) | ||
| Road construction | 1 (12 months) |
AD is a result of multiplying B the number of houses constructed and f the conversion factor.
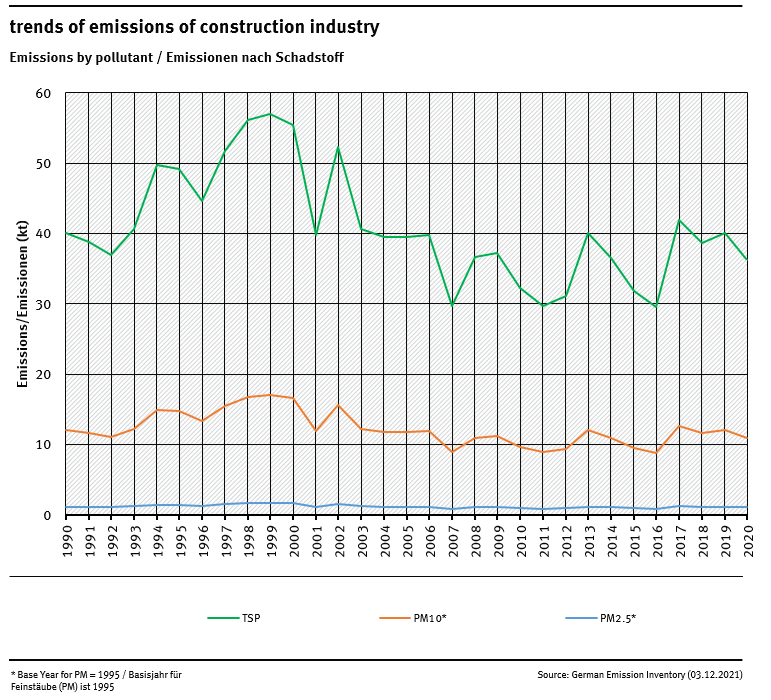
Trends in emissions
All trends in emissions as product of EF and AD correspond to trends of construction activities.
Recalculations
With activity data and emission factors remaining unrevised, no recalculations have been carried out compared to last year's submission.
For pollutant-specific information on recalculated emission estimates for Base Year and 2019, please see the pollutant specific recalculation tables following chapter 8.1 - Recalculations.
Planned improvements
At the moment, no category-specific improvements are planned.
FAQs
Where can I find emissions estimation of demolition activities? - Demolishing without any significant new construction is not covered and there are no other emission factors available for demolition activities only. Nevertheless you can find Information about emissions from 5.E.2 - Other Waste: Building Fires.
Why do German EFs differ from EEA defaults? - It has to do with the default 50% reduction for non-residential buildings and roads (as a result of wetting unpaved temporary roads) that is assumed in the calculations for Germany. This is also already accounted for in the EPA emission factors. It is a result of a control measure that is nearly always taken but in principle optional. In the Guidebook a 50% reduction is advised.