meta data for this page
1.A.3.a ii (i) - Domestic Civil Aviation: LTO
Short description
In NFR category 1.A.3.a ii (i) - Domestic Civil Aviation: LTO emissions from domestic flights between German airports occuring during LTO stage (Landing/Take-off: 0-3,000 feet) are reported.
| Category Code | Method | AD | EF | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.A.3.a ii (i) | T1, T2, T3 | NS, M | CS, D, M | ||||||||||||
| NOx | NMVOC | SO2 | NH3 | PM2.5 | PM10 | TSP | BC | CO | PB | Cd | Hg | Diox | PAH | HCB | |
| Key Category: | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | -/- | - | -/- | - |
In the following, information on sub-category specific AD, (implied) emission factors and emission estimates are provided.
Methodology
Actitvity Data
Specific jet kerosene consumption during LTO-stage is calculated within TREMOD AV as described in the superordinate chapter.
Table 1: Percentual annual fuel consumption during LTO-stage of domestic flights
| 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jet Kerosene | 30.2 | 29.4 | 27.9 | 27.6 | 27.6 | 27.7 | 28.0 | 27.8 | 27.7 | 27.7 | 28.1 | 28.3 | 28.4 | 28.1 | 27.6 | 33.7 |
| Aviation Gasoline | 12.7 | 12.9 | 12.7 | 13.2 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 12.8 | 12.8 | 12.7 | 12.9 | 12.8 | 12.1 | 12.6 | 12.7 | 12.7 | 21.9 |
source: Knörr et al. (2022c) 1) &: Gores (2022) 2)
As explained above, the use of aviation gasoline is - due to a lack of further information - assumed to entirely take place within the LTO-range.
Table 2: annual LTO fuel consumption for domestic flights, in terajoule
| 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jet Kerosene | 8,762 | 8,716 | 8,941 | 8,262 | 8,275 | 8,379 | 8,058 | 7,250 | 7,300 | 7,598 | 7,749 | 7,564 | 7,658 | 7,996 | 3,607 | 3,319 |
| Aviation Gasoline | 245 | 119 | 113 | 71.7 | 56.9 | 65.2 | 58.3 | 52.2 | 49.9 | 58.0 | 47.1 | 44.2 | 44.7 | 37.4 | 24.8 | 31.9 |
| ∑ 1.A.3.a ii (i) | 9,008 | 8,834 | 9,054 | 8,334 | 8,332 | 8,444 | 8,116 | 7,302 | 7,350 | 7,656 | 7,796 | 7,608 | 7,703 | 8,033 | 3,631 | 3,351 |
source: Knörr et al. (2022c) &: Gores (2022)
Emission factors
All country-specific emission factors used for emission reporting were basically ascertained within UBA project FKZ 360 16 029 (Knörr, W., Schacht, A., & Gores, S. (2012)) 3) and have since then been compiled, revised and maintained in TREMOD AV.
Furthermore, the newly implemented EF(BC) have been estimated via f-BCs as provided in the 2019 EMEP/EEA Guidebook 4), Chapter 1.A.3.a, 1.A.5.b Aviation, page 49: “Conclusion”.
For more details, please see the superordinate chapter on civil aviation.
Table 3: Country-specific emission factors, in kg/TJ
| 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JET KEROSENE | ||||||||||||||||
| NH3 | 3.98 | 3.95 | 3.95 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 | 3.97 |
| NMVOC | 28.4 | 28.9 | 30.5 | 32.4 | 32.3 | 31.9 | 32.0 | 34.9 | 37.0 | 36.9 | 36.5 | 38.3 | 39.1 | 40.6 | 58.0 | 65.7 |
| NOx | 295 | 324 | 287 | 277 | 304 | 309 | 312 | 311 | 310 | 312 | 321 | 322 | 316 | 312 | 291 | 280 |
| SOx | 19.7 | 19.5 | 19.5 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 19.6 |
| BC1 | 1.43 | 1.57 | 1.54 | 1.61 | 1.51 | 1.50 | 1.52 | 1.53 | 1.50 | 1.52 | 1.44 | 1.44 | 1.56 | 1.46 | 1.68 | 1.74 |
| PM2 | 2.99 | 3.28 | 3.21 | 3.36 | 3.14 | 3.13 | 3.17 | 3.18 | 3.12 | 3.17 | 3.01 | 2.99 | 3.25 | 3.05 | 3.50 | 3.62 |
| CO | 212 | 211 | 275 | 291 | 260 | 254 | 252 | 260 | 265 | 265 | 252 | 255 | 262 | 268 | 349 | 383 |
| AVIATION GASOLINE | ||||||||||||||||
| NH3 | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE |
| NMVOC | 628 | 635 | 625 | 642 | 631 | 631 | 628 | 632 | 628 | 632 | 627 | 620 | 648 | 660 | 660 | 656 |
| NOx | 87.6 | 87.4 | 87.5 | 85.9 | 85.3 | 87.1 | 87.2 | 87.1 | 87.3 | 85.9 | 87.9 | 88.9 | 88.6 | 92.0 | 92.7 | 90.5 |
| SOx | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 |
| BC1 | 5.91 | 5.92 | 5.97 | 6.21 | 6.31 | 5.94 | 5.92 | 5.92 | 5.88 | 6.15 | 5.79 | 5.60 | 5.71 | 5.13 | 5.01 | 5.39 |
| PM2 | 39.4 | 39.4 | 39.8 | 41.4 | 42.0 | 39.6 | 39.4 | 39.5 | 39.2 | 41.0 | 38.6 | 37.3 | 38.1 | 34.2 | 33.4 | 35.9 |
| TSP3 | 54.6 | 54.6 | 55.0 | 56.6 | 57.2 | 54.8 | 54.6 | 54.7 | 54.4 | 56.1 | 53.8 | 52.5 | 53.2 | 49.4 | 48.6 | 51.1 |
| CO | 17,603 | 17,600 | 17,623 | 17,217 | 17,804 | 17,797 | 17,932 | 17,770 | 17,951 | 17,878 | 17,977 | 18,210 | 17,408 | 17,046 | 17,009 | 17,396 |
1 estimated via a f-BCs (avgas: 0.15, jet kerosene: 0.48) as provided in 5)
2 EF(PM2.5,) also applied for PM10 and TSP (assumption: > 99% of TSP from diesel oil combustion consists of PM2.5)
3 also including TSP from lead: EF(TSP) = 1.6 x EF(Pb) - see road transport
For the country-specific emission factors applied for particulate matter, no clear indication is available, whether or not condensables are included.
For information on the emission factors for heavy-metal and POP exhaust emissions, please refer to Appendix 2.3 - Heavy Metal (HM) exhaust emissions from mobile sources and Appendix 2.4 - Persistent Organic Pollutant (POP) exhaust emissions from mobile sources.
Trend discussion for Key Sources
NFR sub-category 1.A.3.a ii (i) is no key source for emissions.
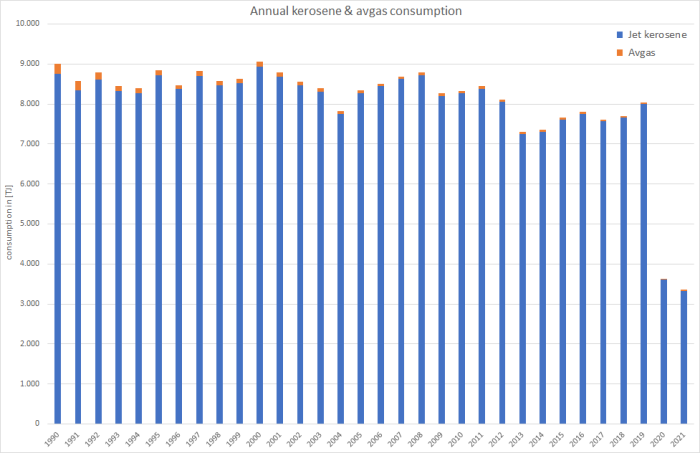
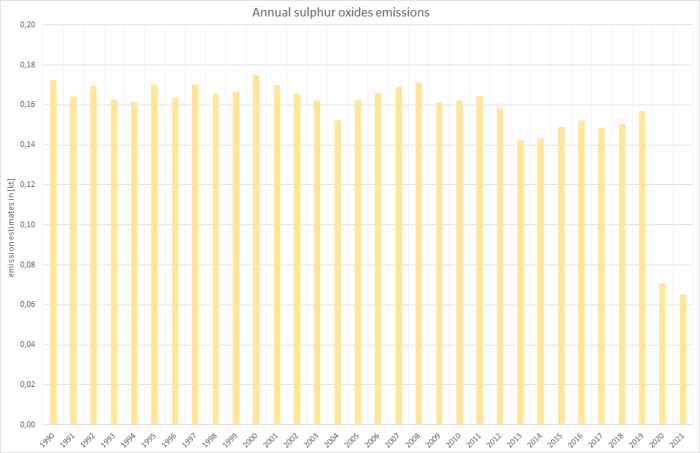
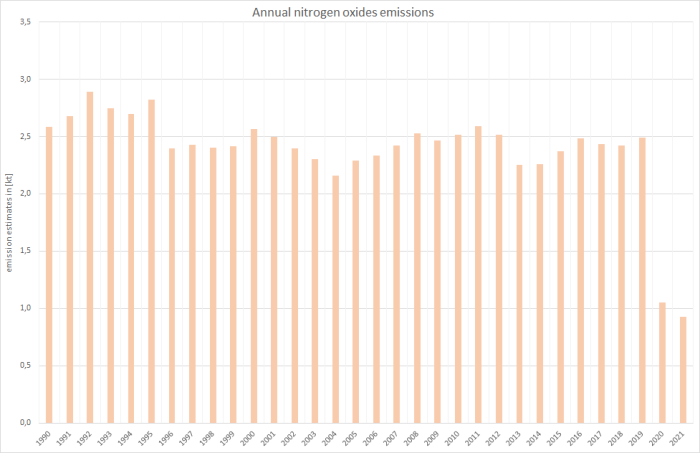
Where, for example, nitrogen oxides and sulphur oxides emissions are dominated by jet kerosene due to the amount of fuel used,…
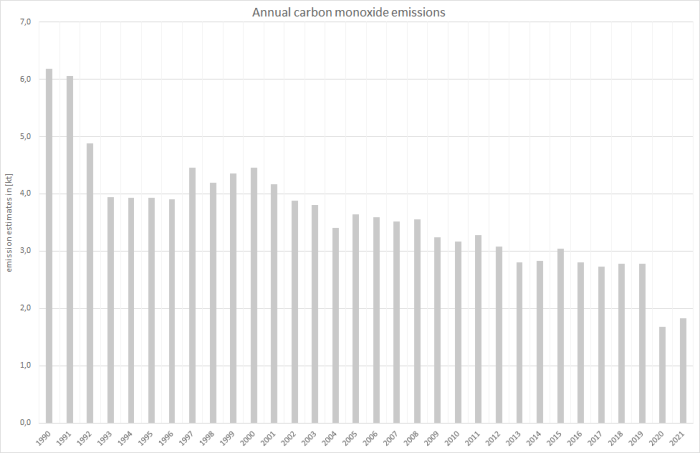
… the majority of carbon monoxide stems from the consumption of avgas given the much higher emission factor applied to this fuel, with the emission trend following the trend in avgas consumption:
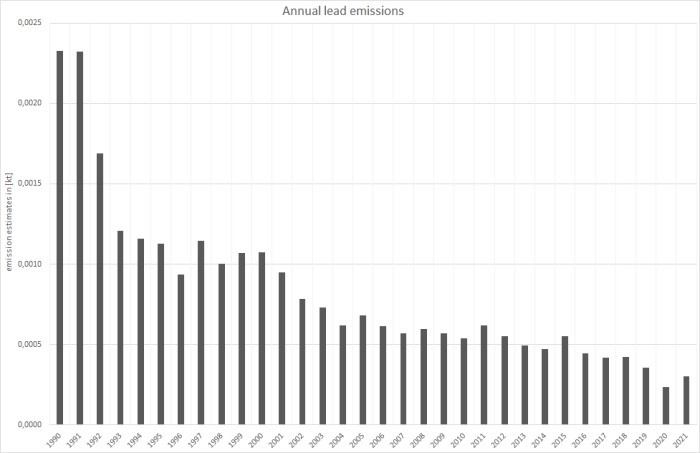
Lead emissions, on the other hand, with no emission factor available for jet kerosene, are only calculated for avgas. Based on a stable fuel lead-content, the emission trend follows the trend in avgas consumption:
Recalculations
Activity data
In order to keep in line with the regularly updated data sets provided to the EEA by Eurocontrol, the average fuel use per LTO cycle has been updated again within TREMOD Aviation but with much smaller impact as in last year's submission.
Furthermore, as explained in the superordinate chapter, avgas consumption for international flights and outside the L/TO range has been estimated for the first time for this submission, with the respective amounts of avgas re-allocated accordingly.
Resulting from this revision, the percentual shares of kerosene consumed during LTO within TREMOD AV have been recalculated as shown in Table 4.
Table 4: Revised percentual share of kerosene and avgas consumed during L/TO for domestic flights, in %
| 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JET KEROSENE | |||||||||||||||
| current submission | 30.2 | 29.4 | 27.9 | 27.6 | 27.6 | 27.7 | 28.0 | 27.8 | 27.7 | 27.7 | 28.1 | 28.3 | 28.4 | 28.1 | 27.6 |
| previous submission | 30.2 | 29.4 | 27.9 | 27.6 | 27.6 | 27.7 | 28.0 | 27.9 | 27.7 | 27.7 | 28.1 | 28.3 | 28.4 | 28.1 | 27.7 |
| absolute change | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -0.02 | -0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -0.01 | -0.01 | -0.01 | -0.01 | -0.02 |
| relative change | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | -0.01% | -0.01% | -0.08% | -0.11% | -0.01% | -0.02% | -0.02% | -0.02% | -0.02% | -0.02% | -0.06% |
| AVGAS | |||||||||||||||
| current submission | 12.7 | 12.9 | 12.7 | 13.2 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 12.8 | 12.8 | 12.7 | 12.9 | 12.8 | 12.1 | 12.6 | 12.7 | 12.7 |
| previous submission | 12.7 | 12.9 | 12.7 | 13.2 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 12.8 | 12.8 | 12.7 | 12.9 | 12.8 | 12.1 | 12.6 | 12.7 | 12.7 |
| absolute change | 0.00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| relative change | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.03% | 0.00% | 0.04% | 0.00% | -0.01% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.01% | 0.01% |
Hence, the amounts of kerosene and avgas allocated to sub-category 1.A.3.a ii (i) had to be revised accordingly:
Table 5: Revised fuel consumption data, in terajoule
| 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JET KEROSENE | |||||||||||||||
| current submission | 8,762 | 8,716 | 8,941 | 8,262 | 8,275 | 8,379 | 8,058 | 7,250 | 7,300 | 7,598 | 7,749 | 7,564 | 7,658 | 7,996 | 3,607 |
| previous submission | 9,380 | 8,303 | 9,811 | 9,187 | 8,589 | 7,869 | 8,171 | 7,633 | 7,297 | 7,358 | 7,844 | 8,210 | 8,362 | 8,476 | 3,867 |
| absolute change | -617 | 412 | -870 | -926 | -315 | 510 | -113 | -383 | 2.78 | 240 | -95 | -646 | -704 | -480 | -260 |
| relative change | -6.58% | 4.97% | -8.87% | -10.07% | -3.66% | 6.47% | -1.39% | -5.02% | 0.04% | 3.26% | -1.21% | -7.87% | -8.42% | -5.66% | -6.73% |
| AVGAS | |||||||||||||||
| current submission | 245 | 119 | 113 | 71.7 | 56.9 | 65.2 | 58.3 | 52.2 | 49.9 | 58.0 | 47.1 | 44.2 | 44.7 | 37.4 | 24.8 |
| previous submission | 245 | 119 | 113 | 71.7 | 56.9 | 65.1 | 58.3 | 52.1 | 49.8 | 58.0 | 47.0 | 44.2 | 44.7 | 37.4 | 24.8 |
| absolute change | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| relative change | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.03% | 0.13% | 0.07% | 0.11% | 0.20% | 0.04% | 0.02% | 0.02% | 0.01% | 0.02% | 0.03% |
In parallel, the majority of country-specific emission factors has been revised within TREMOD AV based on information available from the 2019 EMEP/EEA Guidebook 6) and Eurocontrol's AEM model 7) but cannot be displayed here in a proper way.
For pollutant-specific information on recalculated emission estimates for Base Year and 2020, please see the recalculation tables following chapter 8.1 - Recalculations.
Uncertainties
For uncertainties information, please see main chapter on civil aviation.
For information on uncertainties, please see the main chapter on civil aviation.
Planned improvements
For information on planned improvements, please see main chapter on civil aviation.