meta data for this page
Explanation of Key Trends - Fine Particulate Matter (PM₂.₅)
Obligations
Germany has made a commitment to reduce particulate matter emissions. The revised Gothenburg Protocol and the revised NEC Directive both define emission reduction targets relative to a 2005 base year, mandating 26% (2020) and 43% (2030) reductions respectively.
While Germany's compliance with these obligations is not discussed here, further information on this subject can be found in Chapter 9 - Projections and Chapter 11 - Adjustments and Emission Ceiling Exceedance.
Main drivers
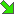
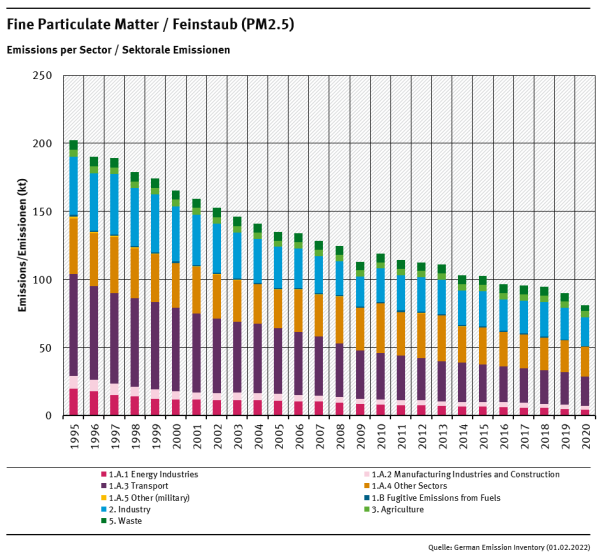
Total PM₂.₅ emissions dropped by 59.9% between 1995 and 2020. The Main Drivers for PM₂.₅ emissions are Fuel Combustion (NFR 1.A) with 72% of total 1995 emissions and a 65% reduction between 1995-2020 and as a sum the Industrial Processes (NFR 2) with about 21% of total 1995 emissions and a 51% reduction between 1995-2020.
Within both National totals and NFR 1.A, Transport (NFR 1.A.3) is responsible for the biggest part of PM₂.₅ emissions. Here, about 77% of 2019 PM₂.₅ transport emissions are induced by Road Transport (NFR 1.A.3.b), caused by two third directly by fuel consumption (NFR 1.A.3.b.i - v) and the other third by road abrasion and tyre and brake wear (NFR 1.A.3.b.vi - vii).
PM₂.₅ Emissions 1990-2020